How to properly prepare the foundation for paving stones?
How to properly prepare the foundation for paving stones?
Before commencing works involving the creation of a subbase for the cube, it is necessary to determine the type of soil and the level of groundwater. This is a very important stage, because the surface needs to be provided with an appropriate drainage system and slope so that water from precipitation does not accumulate.
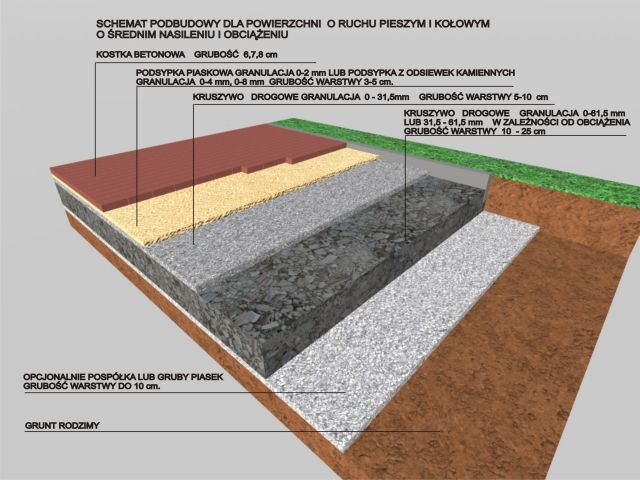
Next, we mark the upper edge of the plane to be laid: for this purpose, you can use metal pins and fishing lines or a rope. Once we have determined the plane of our cube and determined the slopes, we can proceed to remove the native soil. The depth of trenching depends on the type of soil, it is carried out at a depth of 20 cm to 50 cm. The next stage after trenching is leveling the surface of the native soil and shaping the surface to be built in accordance with the gradeline. The leveling process consists in compacting the bottom of the excavation with a roller or compactor, sprinkled with sand or coarse sand (layer up to 10 cm). At this point, the planned bends, turnouts and slopes should be marked out - standard ones are from 0.5 to 3% (depending on the designed drainage system), and any drainage should be installed.
On the subgrade prepared in this way (compacted, hardened and tamped), we place the foundation. If it has a large thickness, its execution should be divided into several stages. Natural or crushed aggregate is most often used to make the foundation. Its thickness depends on the expected surface load and ranges from 20cm (pavement around houses, pavements) to 40cm (pavement for vehicular traffic). The foundation consists of two technological layers: a structural base (load-bearing and frost-resistant layer) and a ballast. The construction layer must be about 1/5 thicker than provided for in the design, because during compaction the aggregate reduces its volume (so-called wedging). The bedding layer is designed to ensure stable seating of each paving stone, it is also used to compensate for possible minimal differences in the height of the stone. It is made of unbound material - sand with a fraction of up to 2 mm or cement-sand mortar. The bedding is not compacted, but leveled with a patch, maintaining appropriate slopes. It should be remembered that the paving stones laid on it should protrude slightly above the planned level of the gradeline, due to the fact that during the compaction of the surface with a vibrator, this layer settles. After compaction, the bedding should be water-permeable, it must not penetrate into the load-bearing layer, and its thickness must be within the range of 2 to 5 cm. A properly made subbase for paving stones should include edging of the surface. The foundation should always be made in accordance with the design and the guidelines of the paving stone manufacturer.
